SlS5H silencing reveals specific pathogen-triggered salicylic acid metabolism in tomato
Abstract: Background
Salicylic acid (SA) is a major plant hormone that mediates the defence pathway against pathogens. SA accumulates in highly variable amounts depending on the plant-pathogen system, and several enzyme activities participate in the restoration of its levels. Gentisic acid (GA) is the product of the 5-hydroxylation of SA, which is catalysed by S5H, an enzyme activity regarded as a major player in SA homeostasis. GA accumulates at high levels in tomato plants infected by Citrus Exocortis Viroid (CEVd), and to a lesser extend upon Pseudomonas syringae DC3000 pv. tomato (Pst) infection.
Results
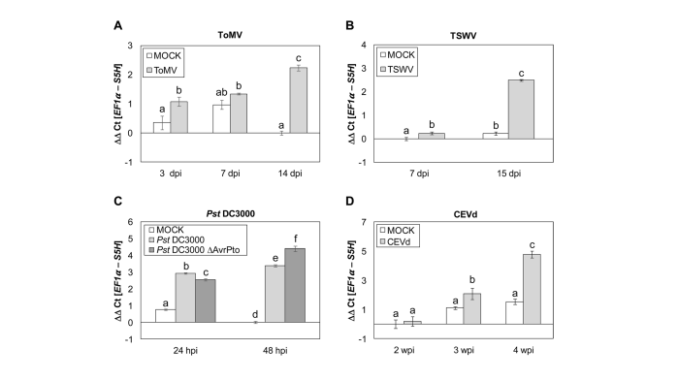
We have studied the induction of tomato SlS5H gene by different pathogens, and its expression correlates with the accumulation of GA. Transient over-expression of SlS5H in Nicotiana benthamiana confirmed that SA is processed by SlS5H in vivo. SlS5H-silenced tomato plants were generated, displaying a smaller size and early senescence, together with hypersusceptibility to the necrotrophic fungus Botrytis cinerea. In contrast, these transgenic lines exhibited an increased defence response and resistance to both CEVd and Pst infections. Alternative SA processing appears to occur for each specific pathogenic interaction to cope with SA levels. In SlS5H-silenced plants infected with CEVd, glycosylated SA was the most discriminant metabolite found. Instead, in Pst-infected transgenic plants, SA appeared to be rerouted to other phenolics such as feruloyldopamine, feruloylquinic acid, feruloylgalactarate and 2-hydroxyglutarate.
Conclusion
Using SlS5H-silenced plants as a tool to unbalance SA levels, we have studied the re-routing of SA upon CEVd and Pst infections and found that, despite the common origin and role for SA in plant pathogenesis, there appear to be different pathogen-specific, alternate homeostasis pathways.
Author(s): Paya, C.; Minguillon, S.; Hernandez, M.; Miguel, S. M.; Campos, L.; Rodrigo, I.; Belles, J. M.; Lopez-Gresa, M. P.; Lison, P.
Bmc Plant Biology
Published: 29 November 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03939-5
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).