Morphological and Electrical Evolution of ZnO:Al Thin Films Deposited by RF Magnetron Sputtering onto Glass Substrates
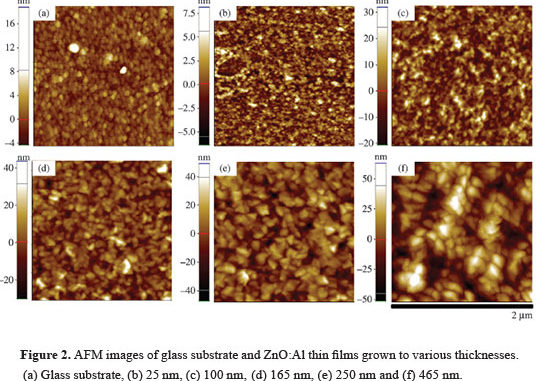
Abstract: In this work, the surface and electrical characteristics ZnO:Al thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering onto glass substrates have been investigated. Analysis of surface morphologies revealed two growth stages. In the first stage, up to thicknesses of 100 nm, the films show surface structures with a granular form without preferential orientation. Beyond thicknesses of 100 nm, however, the grain structures increase in size and height, producing a pyramidal form and preferred orientation along the c-axis. The XRD results show that the films have a preferred orientation in the (002) plane. Furthermore, with the evolution of the film thickness the electrical resistivity decreases to a minimum of 1.6 × 10 – 3 Ω cm for the film of 465 nm thickness. The doping with aluminum atoms produces an increase in concentration of charge carriers to around 8.8 × 1019 cm – 3. All films exhibit high optical transmittance (above 85%) in the visible region.
Author(s): da Silva, Erica Pereira; Chaves, Michel; Durrant, Steven Frederick; et al.
Materials Research-Ibero-American Journal of Materials
Volume: 17 Issue: 6 Pages: 1384-1390 Published: 2014
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.281214