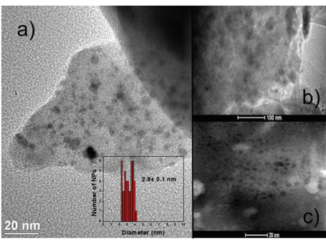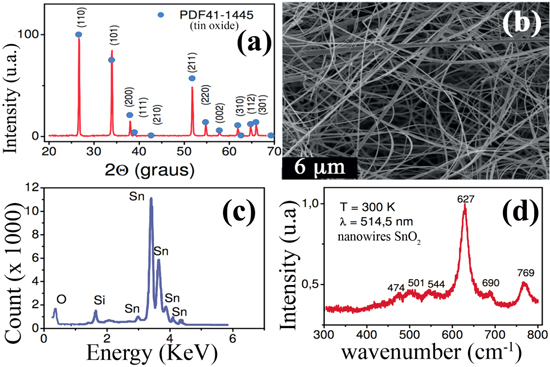
Effect of inhomogeneous Schottky barrier height of SnO2 nanowires device
Abstract: The current–voltage (I–V) characteristics of metal–semiconductor junction (Au–Ni/SnO2/Au–Ni) Schottky barrier in SnO2 nanowires were investigated over a wide temperature range. By using the Schottky–Mott model, the zero bias barrier height Φ B was estimated from I–V characteristics, and it was found to increase with increasing temperature; on the other hand the ideality factor (n) was found to decrease with increasing temperature. The variation in the Schottky barrier and n was attributed to the spatial inhomogeneity of the Schottky barrier height. The experimental I–Vcharacteristics exhibited a Gaussian distribution having mean barrier heights  of 0.30 eV and standard deviation σ s of 60 meV. Additionally, the Richardson modified constant was obtained to be 70 A cm−2 K−2, leading to an effective mass of 0.58m 0. Consequently, the temperature dependence of I–V characteristics of the SnO2 nanowire devices can be successfully explained on the Schottky–Mott theory framework taking into account a Gaussian distribution of barrier heights.
of 0.30 eV and standard deviation σ s of 60 meV. Additionally, the Richardson modified constant was obtained to be 70 A cm−2 K−2, leading to an effective mass of 0.58m 0. Consequently, the temperature dependence of I–V characteristics of the SnO2 nanowire devices can be successfully explained on the Schottky–Mott theory framework taking into account a Gaussian distribution of barrier heights.
Author(s): Amorim, Cleber A.; Bernardo, Eric P.; Leite, Edson R.; et al.
Semiconductor Science and Technology
Volume: 33 Issue: 5 Published: 2018
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1361-6641/aab69e
PDF: Effect of inhomogeneous Schottky barrier height of SnO2 nanowires device