Polaronic ferromagnetic behavior in ClO4- doped poly(3-hexylthiophene) at room temperature
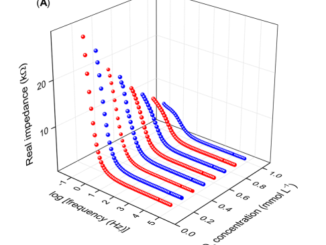
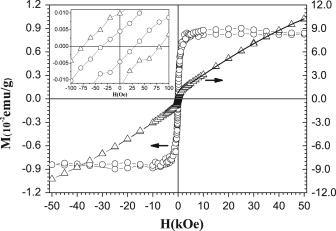
Abstract: The magnetic properties of pressed pellets of ClO4− partially doped poly(3-hexylthiophene) have been investigated in the range from 5 to 300 K and a ferromagnetic phase was observed at room temperature. This behavior was associated to polaron interaction because the saturation magnetization, remanent magnetization, and coercive field, change with the reversible potential that modulates the doping level of the samples. This effect is a consequence of the Nernst potential describes the ratio among reduced sites, polarons and bipolarons in the sample. The results also show that the ferromagnetic phase vanishes when the samples undergo a thermal annealing or are stored under atmospheric conditions for a long period of time. The absence of contaminants such as Co, Fe and Ni was determined using inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry with ppb resolution. These results support that the ferromagnetic behavior observed in samples is intrinsic.
Author(s): de Paula, F. R.; Schiavo, D.; Pereira, E. C.; et al.
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
Volume: 370 Pages: 110-115 Published: 2014
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.06.064
PDF: Polaronic ferromagnetic behavior in ClO4- doped poly(3-hexylthiophene) at room temperature