CO2 mitigation by carbon nanotube formation during dry reforming of methane analyzed by factorial design combined with response surface methodology
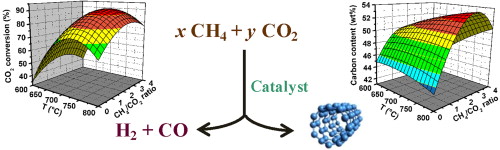
Abstract: A factorial experimental design was combined with response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize the catalyzed CO2 consumption by coke deposition and syngas production during the dry reforming of CH4. The CH4/CO2 feed ratio and the reaction temperature were chosen as the variables, and the selected responses were CH4 and CO2 conversion, the H2/CO ratio, and coke deposition. The optimal reaction conditions were found to be a CH4/CO2 feed ratio of approximately 3 at 700 °C, producing a large quantity of coke and realizing high CO2 conversion. Furthermore, Raman results showed that the CH4/CO2 ratio and reaction temperature affect the system’s response, particularly the characteristics of the coke produced, which indicates the formation of carbon nanotubes and amorphous carbon.
Author(s): Braga, Tiago P.; Santos, Regina C. R.; Sales, Barbara M. C.; et al.
Chinese Journal of Catalysis
Volume: 35 Issue: 4 Pages: 514-523 Published: 2014
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60018-8