Improving the ozone gas-sensing properties of CuWO4 nanoparticles
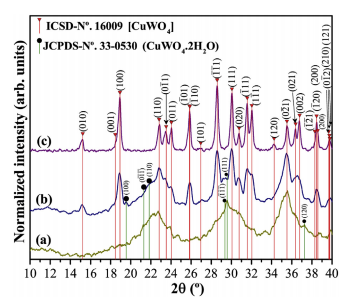
Abstract: This paper consists of an experimental investigation on the effects of annealing temperature on the structural, surface and ozone gas-sensing properties of CuWO4 nanoparticles prepared via a sono-chemical route. X-ray diffraction patterns and X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy revealed that both long-and short-order structures increase with the annealing temperature. Electrical resistance measurements indicated that CuWO4 samples were sensitive in the range of 15-1400 ppb, exhibiting a good reversibility and repeatability. The enhancement of the ozone gas-sensing properties was attributed to the reduction of hydroxyl species and the improvement of the crystallization degree. This study provides a versatile strategy for obtaining CuWO4 nanoparticles for practical applications as an ozone gas sensor. (C) 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Author(s): Catto, AC; Fiorido, T; Souza, ELS; Avansi, W; Andres, J; Aguir, K; Longo, E; Cavalcante, LS; da Silva, LF
JOURNAL OF ALLOYS AND COMPOUNDS
Volume: 748 Pages: 411-417 Published: JUN 5 2018
PDF: Improving the ozone gas-sensing properties of CuWO4 nanoparticles
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.104