Influence of lithium disilicate addition on the dielectric properties of chemically synthesized CaCu3Ti4O12
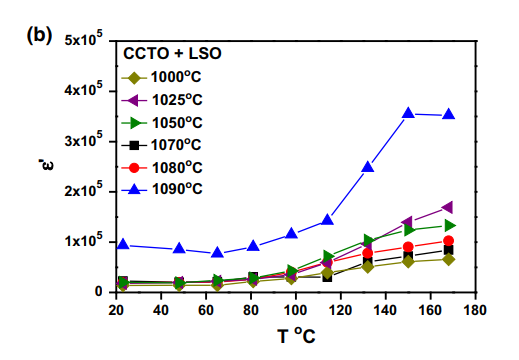
Abstract: The effects of the method of synthesis along with the introduction of a sintering aid on the electric and dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 were investigated in detail. The mixed oxide with perovskite structure was synthesized by the coprecipitation method. Polycrystalline specimens were prepared by adding 0.5 mol% Li2Si2O5 to the mixed oxide followed by sintering in the 1000-1100 A degrees C range for 12 h. A high density value was obtained for sintering at a temperature as low as 1000 A degrees C. Average grain sizes of sintered specimens are of the same order of magnitude as those of specimens prepared by the same method without the additive. The activation energy values for electric conduction were found to be 0.1 eV (grain) and varying from 0.4 to 0.6 eV (grain boundary). The dielectric properties are similar to those of specimens without the additive. The overall results evidence the possibility of reduction of the sintering temperature by about 100 A degrees C with the introduction of a small amount of lithium disilicate while keeping the dielectric properties of pure CaCu3Ti4O12.
Author(s): Porfirio, TC; Muccillo, ENS
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE-MATERIALS IN ELECTRONICS
Volume: 26 Pages: 3970-3975 Published: JUN 2015
DOI: 10.1007/s10854-015-2932-4