NiMoS HDS catalysts – The effect of the Ti and Zr incorporation into the silica support and of the catalyst preparation methodology on the orientation and activity of the formed MoS2 slabs
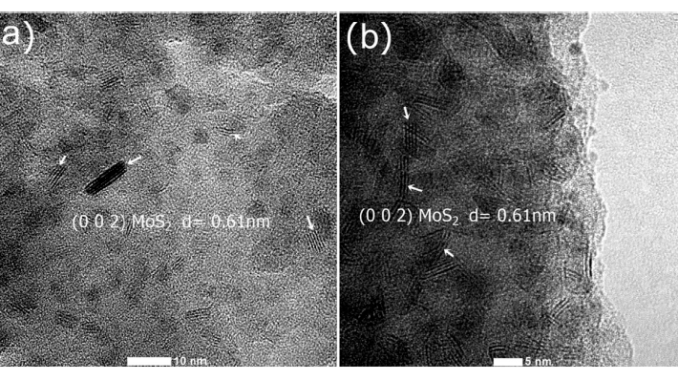
Abstract: HDS NiMo catalyst precursors supported on SiO2, SiO2-TiO2 or SiO2-ZrO2, having high specific surface areas and highly dispersed Mo species were prepared using a one-pot sol-gel methodology or by wet impregnation. After the catalyst precursor sulfidation, HRTEM and Raman analyses evidenced the effective formation of MoS2 slabs on the support. For the NiMoS-Si catalyst (precursor one-pot synthesized), there was a high formation of edge-bonded oriented MoS2 slabs, whereas for the NiMoS/Si prepared by impregnation, basal-bonded MoS2 slabs were more abundant. Coherent with the formation of MoS2 slabs and the promoting effect of Ni, all of the prepared NiMoS catalysts were active in the HDS of thiophene, with those one-pot supported on SiO2 or SiO2-ZrO2 being the most active. Due to, the strong interaction between Mo and Ti, the NiMoS-SiTi catalyst did not show consistent formation of MoS2 slabs and consequently it presented the lowest activity. No observable effect in the HDS activity of the Zr incorporation into the SiO2 framework was noticed. The considerable specific activity (SA) of the catalysts NiMoS-Si and NiMoS/Si, was respectively related to the formation of the most active edge-bonded MoS2 slabs and to the well-active Type II HDS catalysts on multilayer basal-bonded MoS2 slabs. The studied NiMoS-Si and NiMo-SiZr with high SA values evidences that the one-pot sol-gel synthesis methodology used to prepare the catalyst precursor leads to highly active HDS catalysts with the important advantages of reducing the preparation time, energy consumption, and consequently diminishing the catalyst production cost. (C) 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Author(s): Neto, AVD; Leite, ER; da Silva, VT; Zotin, JL; Urquieta-Gonzalez, EA
APPLIED CATALYSIS A-GENERAL
Volume: 528 Pages: 74-85 Published: 2016
DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2016.09.019