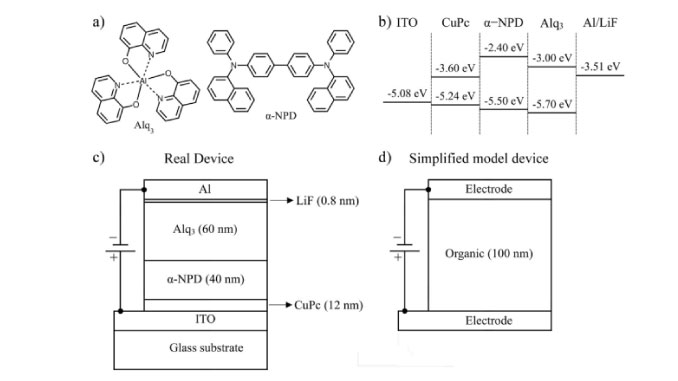
Magnetic field effects in Alq(3)-based OLEDs investigated by electrical impedance spectroscopy
Abstract: The effect of an external magnetic field on electrical impedance was measured on tris-(8hydroxyquinoline) aluminum (Alq(3)) based OLEDs at different temperatures. Magnetic field effects (MFEs) were responsible for significant changes on the real and imaginary components of the impedance, and for the intensification of the negative capacitance (NC) effect. The observed MFEs do not present a strong temperature dependence. Simulations via equivalent circuits and numerical solutions of Boltzmann transport equations in a drift-diffusion approximation and employing small sinusoidal signal analysis indicate that such effects are consistent with an enhancement of the carrier mobilities and a quenching of the recombination rates. Such changes lead to reduced resistance and more intense NC effects on the device. The results were interpreted in terms of the currently accepted OMAR models: electron-hole pair model, triplet-polaron reaction mechanism and bipolaron model.
Author(s): Nunes-Neto, O (Nunes-Neto, Oswaldo); Batagin-Neto, A (Batagin-Neto, Augusto); Leite, DMG (Leite, Douglas M. G.); Nuesch, FA (Nuesch, Frank A.); Graeff, CFO (Graeff, Carlos F. O.)
ORGANIC ELECTRONICS
Volume: 50 | Pages: 347-358 | Published: NOV 2017
PDF: Magnetic field effects in Alq(3)-based OLEDs investigated by electrical impedance spectroscopy
DOI: 10.1016/j.orgel.2017.08.003