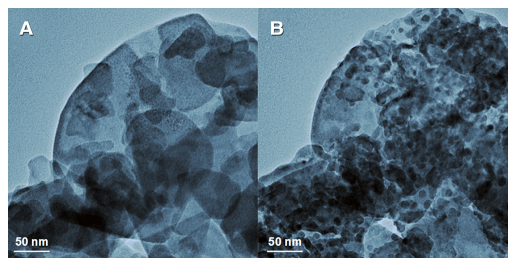
In Situ Growth of Bi Nanoparticles on NaBiO3, delta-, and beta-Bi2O3 Surfaces: Electron Irradiation and Theoretical Insights
Abstract: Herein, we present a combined experimental and theoretical study of the in situ growth of Bi nanoparticles on NaBiO3, delta-, and beta-Bi2O3 surfaces mediated by the electron beam of a high-resolution transmission electron microscope. Density functional theory and quantum theory of atoms in molecule calculations were used to gain a deeper insight into the experimental observations and to provide an atomistic basis for understanding the formation mechanism of Bi NPs on NaBiO3, delta-, and beta-Bi2O3 under electron beam irradiation. Analysis of the experimental data and electron density distributions suggests that the formation of Bi NPs can be related to the structural and electronic changes occurring within the octahedral [BiO6] clusters, and to a lesser extent, [NaO6] clusters, which serve as the constituent building blocks of NaBiO3. Our findings indicate that as a function of the number of added electrons, the formation of beta-Bi2O3 takes place first followed by the subsequent appearance of metallic Bi NPs generated in the crystal by electron beam irradiation.
Author(s): Assis, M; de Oliveira, MC; Machado, TR; Macedo, NG; Costa, JPC; Gracia, L; Andres, J; Longo, E
JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY C
Volume: 123 Pages: 5023-5030 Published: FEB 28 2019
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11566