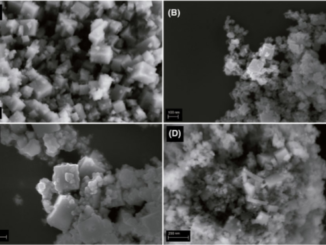
Effect of different synthesis methods on the morphology, optical behavior, and superior photocatalytic performances of Ag3PO4 sub-microcrystals using white-light-emitting diodes
Abstract: In this paper, we report on the superior photocatalytic properties of silver orthophosphate (Ag3PO4) sub-microcrystals prepared using different synthesis methods: precipitation (PM), precipitation-calcination (PM-C), and precipitation-hydrothermal (PM-H), on the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) cationic dye and methyl orange (MO) anionic dye using white-light-emitting diodes (WLEDs). The structure of the Ag3PO4 sub-microcrystals obtained was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Rietveld refinement, micro-Raman (M-Raman), and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was used to investigate the surface chemical composition and states. The shape, average crystal size, and morphological changes were observed using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The results indicated that all samples have cubic body-centered, P 43 n (218) space group, with the following crytallite size: PM (103.4 nm), PM-C (56.7 nm) and PM-H (123.8 nm). Also, it was observed the optical band gap values of 2.23, 2.15 and 2.16 eV of the samples PM, PM-C and PM-H, respectively. For both dyes, the PM-C sample has higher photodegradation efficiency (98%) and apparent quantum efficiency (phi(x) = 0.081) in relation to PM and PM-H samples. In addition, especially to RhB, the apparent quantum efficiency of samples practically remains unchanged by three photocatalytic cycles due to use of white light emitting diode (WLEDs) illumination.
Author(s): Cruz, JF; Costa, TMS; Lima, MS; Silva, LJ; Santos, RS; Cavalcante, LS; Longo, E; Luz, GE
JOURNAL OF PHOTOCHEMISTRY AND PHOTOBIOLOGY A-CHEMISTRY
Volume: 377 Pages: 14-25 Published: MAY 15 2019
DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.03.031