Cluster Coordination and Photoluminescence Properties of α-Ag2WO4 Microcrystals
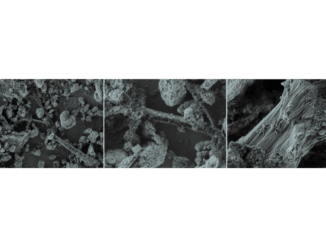
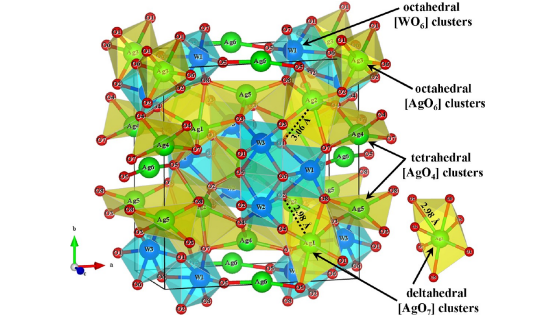
Abstract: In this paper, we report our initial research to obtain hexagonal rod-like elongated silver tungstate (α-Ag2WO4) microcrystals by different methods [sonochemistry (SC), coprecipitation (CP), and conventional hydrothermal (CH)] and to study their cluster coordination and optical properties. These microcrystals were structurally characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Rietveld refinements, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES), and extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) spectroscopies. The shape and average size of these α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals were observed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The optical properties of these microcrystals were investigated by ultraviolet–visible (UV–vis) spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) measurements. XRD patterns and Rietveld refinement data confirmed that α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals have an orthorhombic structure. FT-IR spectra exhibited four IR-active modes in a range from 250 to 1000 cm–1. XANES spectra at the W L3-edge showed distorted octahedral [WO6] clusters in the lattice, while EXAFS analyses confirmed that W atoms are coordinated by six O atoms. FE-SEM images suggest that the α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals grow by aggregation and the Ostwald ripening process. PL properties of α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals decrease with an increase in the optical band-gap values (3.19–3.23 eV). Finally, we observed that large hexagonal rod-like α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals prepared by the SC method exhibited a major PL emission intensity relative to α-Ag2WO4 microcrystals prepared by the CP and CH methods.
Author(s): Cavalcante, L. S. ; Almeida, M. A. P. ; Avansi, Jr., W. ; Tranquilin, R. L.; Longo, E.; Batista, N. C.; Mastelaro, V. R.; Li, M. Siu
Inorg. Chem.
Published: September 21, 2012