Investigation of the influence of the void fraction on the energy consumption of a vertical electrolyser under natural convection
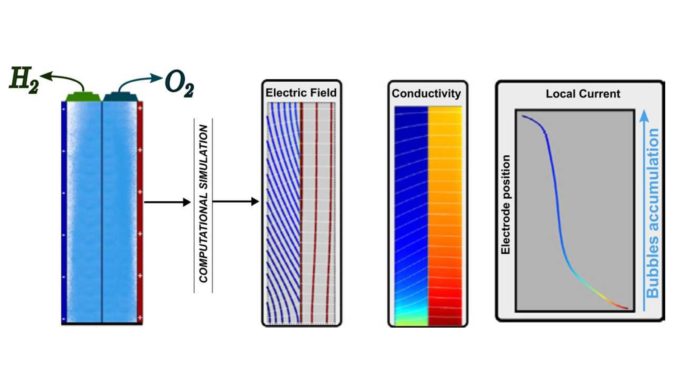
Abstract: The ongoing need to develop and enhance current energy sources to replace fossil fuels emphasizes the necessity of a thorough understanding of clean energy production methods such as hydrogen production via water electrolysis. This work provides a versatile CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) simulation that describes an alkaline water electrolyzer, which considers the electrolyte’s performance, electrode materials, separator membrane, and the impact of generated bubbles in the electrolysis considering anodic and cathodic reactions at the same time. The bubble presence affects the applied cell potential and the local current distribution, and it is directly related to the efficiency of the process. For a multivariate view, a 23 factorial design was carried out, in which electrode material, applied current density, and the presence or absence of gas bubbles were simultaneously investigated. As a result, the contribution of each factor to the cell potential was calculated, their link to the applied current, and the cross-effects. Finally, we observed an important non-uniformity in the local current distribution and an increase in the spent energy due to the produced gases at current densities higher than 100 mA cm−2.
Author(s): Wosiak, G.; Silva, J.; Sena, S.S.; Carneiro-Neto, E.B.; Lopes, M.C.; Pereira, E.
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering
Published: June 2022, Volume 10, Issue 3, 107577
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107577
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).