Study of CaTiO3–ZnS heterostructure obtained by microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis and its application in photocatalysis
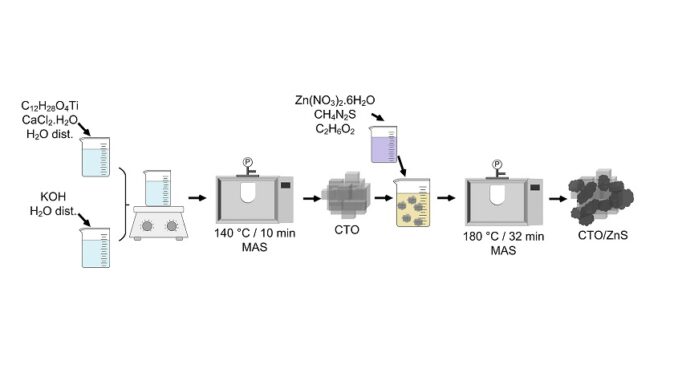
Abstract: We report herein the assembly of a calcium titanate (CTO)-zinc sulfide (ZnS) heterostructure through a microwave-assisted solvothermal (MAS) method and its respective characterizations to evaluate its material properties and applicability in heterogeneous photocatalysis. The CTO-ZnS heterostructure comprises a mixture of the orthorhombic crystalline phase of CTO and the cubic crystalline phase of ZnS. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images have revealed that the CTO consists of mesocrystals assembled from agglomerated microcubes. After applying a ZnS coating, it was possible to identify the formation of a cloud of particles around parts of the CTO mesocrystals, thus forming the heterostructure. The presence of ZnS on the CTO surface allowed for greater emission of photoluminescence, resulting in improved efficiency for photocatalytic applications. Photodegradation tests on Rhodamine B (RhB) dye in the presence of CTO, ZnS, and CTO-ZnS revealed that the heterostructure led to more extensive photocatalytic degradation (50.5%) within 30 min than CTO (10%). Moreover, the degradation efficiency over the CTO-ZnS increased to 95.7% after 180 min, indicating that the ZnS coating served to increase the degree of discoloration over time. These satisfactory results demonstrate that CTO-ZnS is a promising photocatalyst capable of accelerating the degradation of organic dyes, thus contributing to the decontamination of water resources. Scavenger tests revealed holes (h+) to be the main active species in the photocatalytic process with CTO, whereas electrons (e−), h+, and hydroxyl radicals (HO*) are all involved in the mechanism with both CTO-ZnS and ZnS.
Author(s): Ucker, C. L.; Almeida, S. R.; Cantoneiro, R. G.; Diehl, L. O.; Cava, S.; Moreira, M. L.; Longo, E.; Raubach, C. W.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids
Published: January 2023, Volume 172, 111050
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2022.111050
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).