Phase transformation/stabilization and ionic conductivity in tantalum oxide co-doped zirconia-scandia solid electrolyte
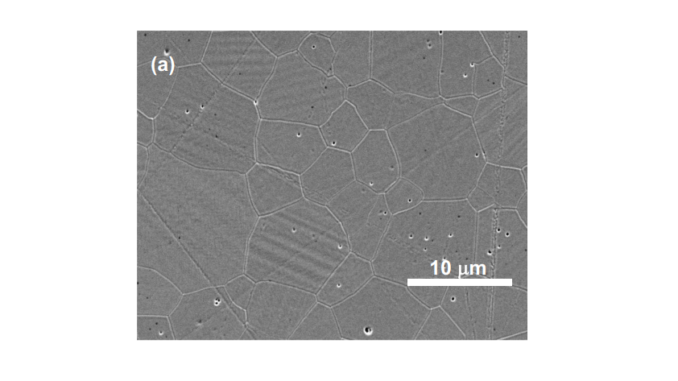
Abstract: The influence of small amounts of tantalum oxide as co-dopant on phase transformation and stabilization, microstructure and ionic conductivity of zirconia-10 mol% scandia is reported in this work. Cylindrical pellets were prepared by solid state synthesis with sintering at 1500 °C for 5 h. High relative density values (> 95%) were achieved. Reduction of the enthalpy for the cubic ⇌β-rhombohedral phase transformation was found for increasing amounts of the co-dopant. Full stabilization of the cubic structure at room temperature was obtained with only 0.45 mol% tantalum oxide addition. The ionic conductivity of sintered specimens was investigated as a function of the temperature and oxygen partial pressure by impedance spectroscopy. The fully stabilized co-doped system revealed a pure ionic conduction behavior up to 800 °C with wide electrolytic domain. In the 700–800 °C range, the ionic conductivity of co-doped specimens is similar to that of pure zirconia-scandia.
Author(s): Souza, J. P.; Fujimoto, T. G.; Batista, R. M.; Steil, M. C.; Muccillo, R.; Muccillo, E. N. S.
Ionics
Published: 13 May 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04604-5
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).