Development of a nanocomposite chemiresistor sensor based on pi-conjugated azo polymer and graphene blend for detection of dissolved oxygen
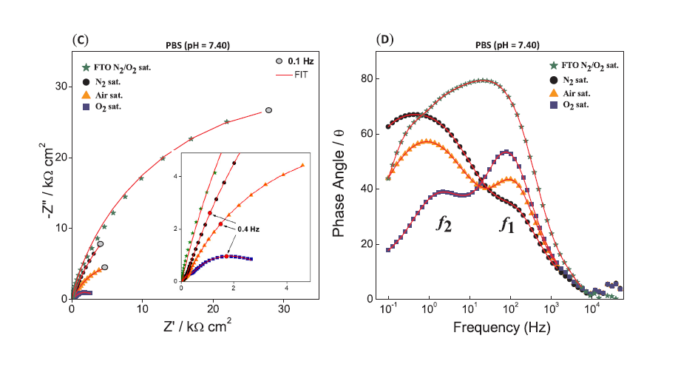
Abstract: The present paper describes the electrochemical impedance activity of a hybrid film with graphene and poly(azo-Bismarck Brown Y) as the chemiresistor material. This nanocomposite film exhibits interesting properties based on the redox properties of the azo polymer combined with the great electronic conductivity and stability of graphene. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at the poly(azo-BBY)-rGO electrode in solutions with different dissolved O2 concentrations revealed that the resistance values are very sensitive to variations in the O2 concentration.
Author(s): Oliveira, A. O., Teixeira M.F.S.
Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical
Volume: 271 Pages: 353-357 Published: 2018.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.128