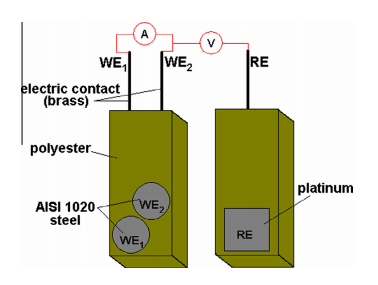
Corrosion of AISI 1020 steel in crude oil studied by the electrochemical noise measurements
Abstract: In this work, the corrosion process of AISI 1020 in crude oil, to which different amounts of sea water (0.5 and 4.0% v/v), naphthenic acid (500 and 3000 ppm), and H2S (50 and 1000 ppm) were added, was investigated using electrochemical noise at open circuit potential. The different oil samples were prepared using a 2(3) factorial design involving the three species described above. To analyze the obtained data, wavelet transform and energy distribution plot were used. Using this technique it was possible to separate the contributions of two types of corrosion, generalized and localized, in oil samples with different compositions and to analyze the effect of those variables on the changes that occurred during 55 days of immersion in the experiment. The results showed an increase in pitting formation in those steel samples studied in oil containing H2S at 50 ppm and 4.0% sea water. The contribution of generalized corrosion on the metallic surface is higher in oil containing 3000 ppm naphthenic acid than in the other experimental conditions. The results were confirmed by morphological analysis of the corroded samples. (C) 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Author(s): Rios, EC; Zimer, AM; Mendes, PCD; Freitas, MBJ; de Castro, EVR; Mascaro, LH; Pereira, EC
FUEL
Volume: 150 Pages: 325-333 Published: JUN 15 2015
PDF: Corrosion of AISI 1020 steel in crude oil studied by the electrochemical noise measurements
DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.022