Phosphate glasses via coacervation route containing CdFe2O4 nanoparticles: structural, optical and magnetic characterization
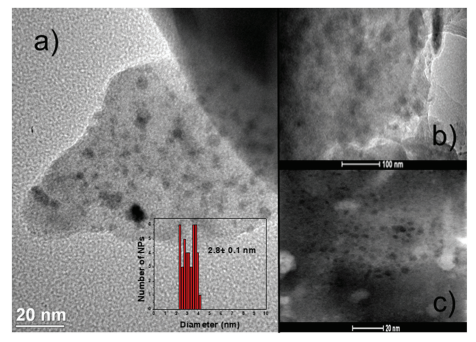
Abstract: CdFe2O4 nanoparticles of around 3.9 nm were synthesized using the coprecipitation method and protected by a silica layer. The nanoparticles were mixed with a coacervate and transformed into phosphate glasses with 1, 4 and 8% in mass of nanoparticles by the melt-quenching method. TEM images confirm that the nanoparticles were successfully incorporated into the matrix without inducing crystallization. P-31 NMR and Raman spectral analyses show that new P-O-Si bonds are formed in the glasses containing nanoparticles. The glass transition increases as a function of the nanoparticle content due to an increase in the connectivity of the phosphate glass chains. The UV-Vis spectra show bands at 415 and 520 nm assigned to Fe3+ ions and at 1025 nm, characteristic of Fe2+ ions, indicating that some of the nanoparticles dissolve during the melting process. The sample with 8% CdFe2O4 presents a paramagnetic behavior. The glasses obtained are transparent, non-hygroscopic and possess enormous thermal stability which is important for the production of optical devices.
Author(s): Orives, JR; Viali, WR; Santagneli, SH; Afonso, CRM; Carvalho, MH; de Oliveira, AJA; Nalin, M
DALTON TRANSACTIONS
Volume: 47 Pages: 5771-5779 Published: APR 28 2018
DOI: 10.1039/c8dt00560e