Bisphosphonates on Smooth TiO2: Modeling and Characterization
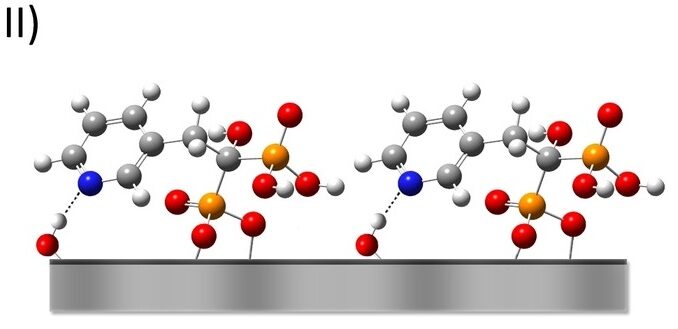
Abstract: Bisphosphonates adsorbed on TiO2 were investigated in this work. Molecules can vary their reactivity according to medium and deprotonation. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy demonstrated that functionalization occurs in a short time and resulted in a predominantly “side-on” adsorbate configuration after two hours of immersion. The surface is negatively charged due to deprotonated phosphonates, as demonstrated by zeta potential. Molecules adsorb following surface topography, unchanging surface roughness. This paper presents insights into surfaces properties of sputter-deposited titania modified with bisphosphonates, including zeta potential measurements in a pH range. Functionalization was investigated through simulation and experimental approaches to model the adsorbate and evaluate structure-response relationships. Molecules of etidronic, alendronic, and risedronic acids were investigated through density functional theory. The molecules vary their reactivity through similar structures considering different scenarios. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of titania/BP systems demonstrated that functionalization occurs in a short time and resulted in a predominantly “side-on” adsorbate configuration after two hours of immersion. Zeta potential showed the predominancy of negative charges deprotonated free phosphonates. Water contact angle demonstrated that titania surfaces are hydrophilic after overnight functionalization. Atomic force measurements of bisphosphonates layers suggested that the molecular anions follow the surface topography, unchanging the surface roughness.
Author(s): Dias, L. F. G.; Rheinheimer, J. P. C.; Gomes, O. P.; Noeske, M.; Stamboroski, S.; Bronze-Uhle, E. S.; Mainardi, M. C.; Cavalcanti, W. L.; Neto, A. B.; Lisboa, P. N.
Chemistryselect
Published: 20 April 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202200286
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).