Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from wastewater using graphene-based nanomaterials synthesized by conventional chemistry and green synthesis: A critical review
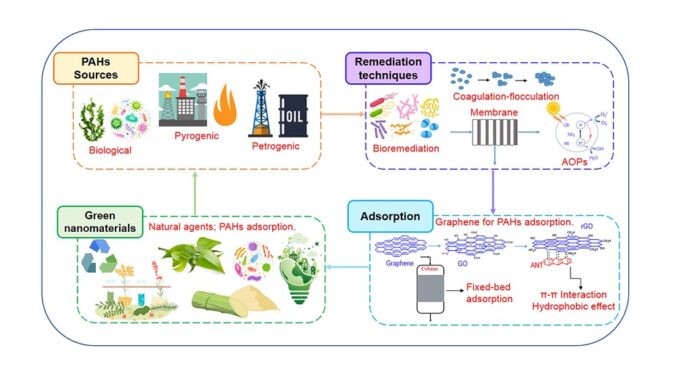
Abstract: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are organic pollutants formed mainly by the incomplete combustion of organic matter, such as oil, gas and coal. The presence of PAHs can cause irreparable damage to the environment and living beings, which has generated a global concern with the short and long term risks that the emission of these pollutants can cause. Many technologies have been developed in the last decades aiming at the identification and treatment of these compounds, mainly, the PAHs from wastewater. This review features an overview of studies on the main methods of PAHs remediation from wastewater, highlighting the adsorption processes, through the application of different adsorbent nanomaterials, with a main focus on graphene-based nanomaterials, synthesized by conventional and green routes. Batch and fixed-bed adsorptive processes were evaluated, as well as, the mechanisms associated with such processes, based on kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Based on the studies analyzed in this review, green nanomaterials showed higher efficiency in removing PAHs than the conventional nanomaterials. As perspectives for future research, the use of green nanomaterials has shown to be sustainable and promising for PAHs remediation, so that further studies are needed to overcome the possible challenges and limitations of green synthesis methodologies.
Author(s): ueiroz, R. N.; Carlos da Silva, M. G.; Mastelaro, V. R.; Prediger, P.; Adeodato Vieira, M. G.
Journal of Hazardous Materials
Published: 15 January 2022, Volume 422, 126904
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126904
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).