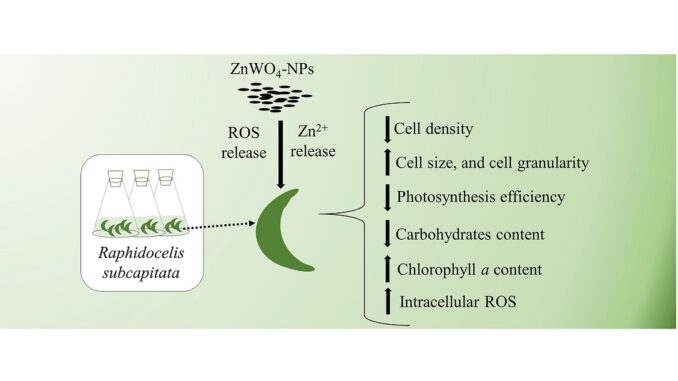
Effects of ZnWO4 nanoparticles on growth, photosynthesis, and biochemical parameters of the green microalga Raphidocelis subcapitata
Abstract: Nanoparticles have applications in many sectors in the society. ZnWO4 nanoparticles (ZnWO4-NPs) have potential in the fabrication of sensors, lasers, and batteries, and in environmental remediation. Thus, these NPs may reach aquatic ecosystems. However, we still do not know their effects on aquatic biota and, to our knowledge, this is the first study that evaluates the toxicity of ZnWO4-NPs in a eukaryotic organism. We evaluated the toxicity of ZnWO4-NPs on the green microalga Raphidocelis subcapitata for 96 h, in terms of growth, cell parameters, photosynthesis, and biochemical analysis. Results show that most of Zn was presented in its particulate form, with low amounts of Zn2+, resulting in toxicity at higher levels. The growth was affected from 8.4 mg L−1, with 96h–IC50 of 23.34 mg L−1. The chlorophyll a (Chl a) content increased at 30.2 mg L−1, while the fluorescence of Chl a (FL3-H) decreased at 15.2 mg L−1. We observed increased ROS levels at 44.4 mg L−1. Regarding photosynthesis, the NPs affected the oxygen evolving complex (OEC) and the efficiency of the photosystem II at 22.9 mg L−1. At 44.4 mg L−1 the qP decreased, indicating closure of reaction centers, probably affecting carbon assimilation, which explains the decay of carbohydrates. There was a decrease of qN (non-regulated energy dissipation, not used in photosynthesis), NPQ (regulated energy dissipation) and Y(NPQ) (regulated energy dissipation via heat), indicating damage to the photoprotection system; and an increase in Y(NO), which is the non-regulated energy dissipation via heat and fluorescence. The results showed that ZnWO4-NPs can affect the growth and physiological and biochemical parameters of the chlorophycean R. subcapitata. Microalgae are the base of aquatic food chains, the toxicity of emerging contaminants on microalgae can affect entire ecosystems. Therefore, our study can provide some help for better protection of aquatic ecosystems.
Author(s): Renan Castelhano Gebara, Cínthia Bruno de Abreu, Giseli Swerts Rocha, Adrislaine da Silva Mansano, Marcelo Assis, Ailton José Moreira, Mykaelli Andrade Santos, Thalles Maranesi Pereira, Luciano Sindra Virtuoso, Maria da Graça Gama Melão, Elson Longo
Chemosphere
Published: April 2024, Volume 353, 141590
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141590
CDMF
The CDMF, hosted at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar), is one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDC) supported by the São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (Fapesp), and also receives investment from the National Council Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), from the National Institute of Science and Technology of Materials in Nanotechnology (INCTMN).