Writers: Zahid H. Chohan, Marcelo Zaldini Hernandes, Fabricio R. Sensato, Diogo Rodrigo Magalhaes Moreira, Valéria Rego Alves Pereira, Juliana Kelle de Andrade Lemoine Neves, Andresa Pereira de Oliveira, Beatriz Coutinho de Oliveira & Ana Cristina Lima Leite
Keywords: Cobalt, copper, DFT, metal complexes, prodrugs, sulfonamides, Trypanosoma cruzi
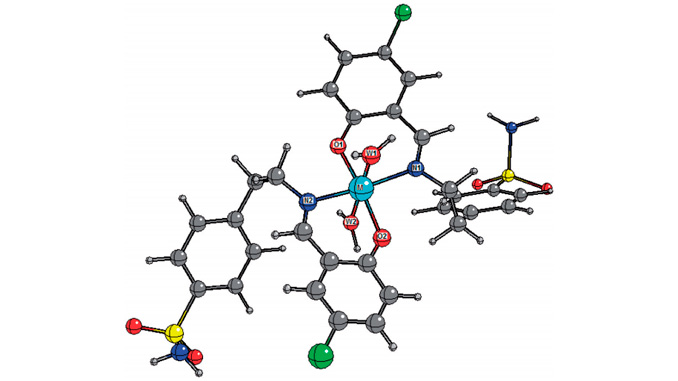
Abstract: In this article, we describe that mononuclear complexes composed of (5-chloro-2-hydroxybenzylidene) aminobenzenesulfonamides (L1–3) of general formula (L2(M)2H2O, where M is Co, Cu, Zn, Ni or Mn) reduced epimastigote proliferation and were found cidal for trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi Y strain. Complexes C5 and C11 have IC50 of 2.7 ± 0.27 and 4.8 ± 0.47 µM, respectively, for trypomastigotes, when the positive control Nifurtimox, which is also an approved drug for Chagas disease, showed IC50 of 2.7 ± 0.25 µM. We tested whether these complexes inhibit the enzyme T. cruzi trypanothione reductase or acting as DNA binders. While none of these complexes inhibited trypanothione reductase, we observed some degree of DNA binding, albeit less pronounced than observed for cisplatin in this assay. Unfortunately, most of these complexes were also toxic for mouse splenocytes. Along with the present studies, we discuss a number of interesting structure–activity relationships and chemical features for these metal complexes, including computational calculations.