Writers: Paulo A. Raymundo-Pereira; Ana C. V. Mascarenhas; Marcos F. S. Teixeira
Keywords: Biosensor; Electrochemical
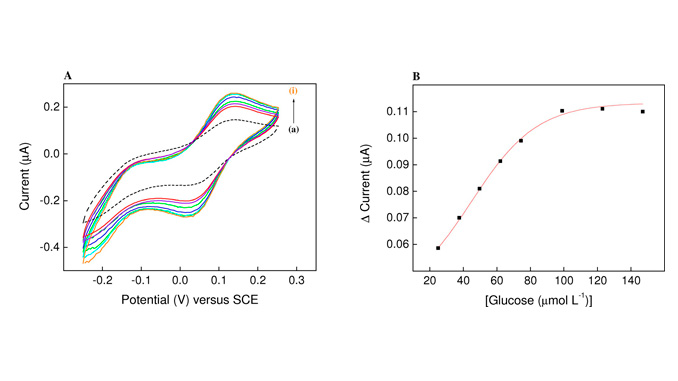
Abstract: The mediation of electron-transfer by oxo-bridged dinuclear ruthenium ammine [(bpy)2(NH3)RuIII(µ-O)RuIII(NH3)(bpy)2]4+ for the oxidation of glucose was investigated by cyclic voltammetry. These ruthenium (III) complexes exhibit appropriate redox potentials of 0.131–0.09 V vs. SCE to act as electron-transfer mediators. The plot of anodic current vs. the glucose concentration was linear in the concentration range between 2.52×10−5 and 1.00×10−4 mol L−1. Moreover, the apparent Michaelis-Menten kinetic (KMapp) and the catalytic (Kcat) constants were 8.757×10−6 mol L−1 and 1,956 s−1, respectively, demonstrating the efficiency of the ruthenium dinuclear oxo-complex [(bpy)2(NH3)RuIII(µ-O)RuIII(NH3)(bpy)2]4+ as mediator of redox electron-transfer.