Writers: R. A. Silva and M. O. Orlandi
Keywords: Sensor; Nanostructures; Synthesis
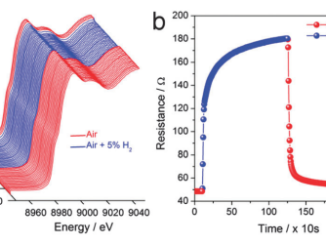
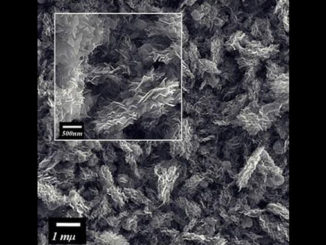
Abstract: ZnO nanostructures were synthesized using two different routes and the light sensor response of structures was studied. The synthesis by carbothermal reduction resulted in ZnO tetrapods while the synthesis by microwave assisted hydrothermal method produced multipoint stars structures. Characterization by scanning and transmission electron microscopy confirmed that both structures consist of one-dimensional crystals with a hexagonal cross section and growth direction. Under a simulated solar radiation spectrum, it was observed that tetrapods display a light sensor response of approximately 5000. For the multipoint stars, a maximum in the sensor signal value of 3400 was achieved, which also represents a substantial variation in the conductivity of the material. A model based on the surface oxygen presence is proposed to explain the observed results.