Writers: Osmair Vital de Oliveira and Luciano Tavares Costa and Edson Roberto Leite
Keywords: Polymer nanocomposite; Solvent effect; Molecular dynamics simulation
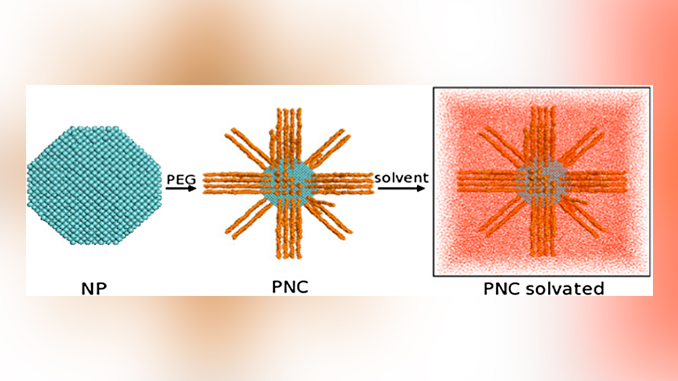
Abstract: Grafted polymer on nanoparticle is an efficient way to obtain/improve aggregation, solubility, form and size of nanoparticles. In the present work molecular dynamics simulations were carried out to study a polyethylene glycol (PEG) based nanocomposite model in which the polymer is filled with Fe3O4 nanoparticle in water and chloroform solvents. Radial distribution function (RDF), dihedral distribution function, end-to-end distance and radius of gyration analysis indicate that the structural properties of the pure polymer is similar when attached to the nanoparticle. Due to the high polymer density a compact shell is formed around the nanoparticle surface in chloroform (poor solvent). Contrary, in water (good solvent), the polymer chains adopt an extended conformation due to entropic effects. Furthermore, the polymer structure in the nanocomposite is similar to that one founded in the solvents considered. Finally, the results corroborate to the hypothesis of the transferability of the polymer properties to the nanoparticle in solution.