A Synaptic Electrochemical Memristor Based on the Cu2+/Zn2+Cation Exchange in Zn:CdS Thin Films
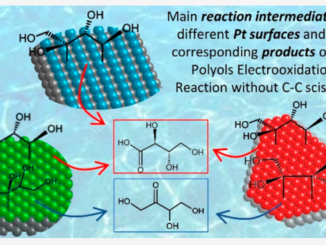
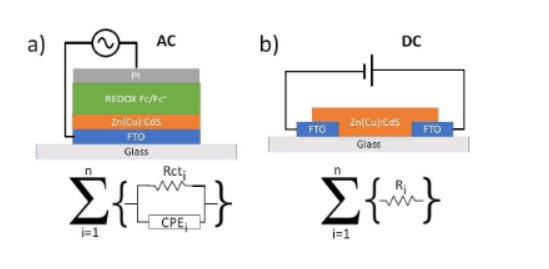
Abstract: Neuromorphic hardware systems that simulate functions of biological brain synapses have been widely investigated due to their possible application in brain-inspired computing. We hereby report on a novel electrochemical state machine based on Zn:CdS thin films. The memory switching mechanism involves the cation exchange of Cu2+ and Zn2+ acting as inorganic “neurotransmitters”. Similarly to the synapse-neuro- transmitter interactions, Cu2+ ions increase the conductivity and the electrocatalytic activity of Zn:CdS towards the ferrocene/ferrocenium redox process. The cationic substitution of Zn2+ by Cu2+ in the film has shown significant changes in the electrochemical characteristic of the device. Such effects have been investigated with both alternated current (impedance) and direct current (voltammetry and I vs V) measurements. The cation exchange mechanism allows to write and store an electrochemical information into the device. Such information can be gradually erased by exchanging the absorbed Cu2+ ions with Zn2+. By means of a timed soaking, of the active area, with Cu2+ and Zn2+ diethyldithiocarbamates, the device can be driven through multiple conduction states, making it suitable for applications in artificial synapses research and memory storage systems.
Author(s): Congiu, Mirko; Boratto, Miguel H.; Graeff, Carlos F. O.
Chemistryselect
Volume: 3 Issue: 34 Pages: 9794-9802 Published: 2018
DOI: 10.1002/slct.201801152
PDF: A Synaptic Electrochemical Memristor Based on the Cu2+Zn2+ Cation Exchange in ZnCdS Thin Films