Alkali Cation Effect During the Oscillatory Electroreduction of H2O2 on Pt
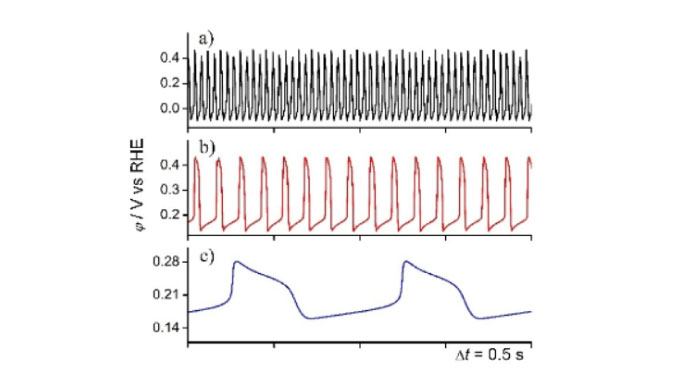
Abstract: Hydrogen Peroxide Reduction Reaction (HPRR) catalyzed by Pt was studied in alkaline media and the effect of alkali cations were analyzed by the changes on dynamic instabilities presented by this system under high ohmic drop conditions. The origin of these instabilities is the competition between OH2- electroreduction and hydrogen adsorption on Pt surfaces, the latter being the first step for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). Both HER and hydrogen adsorption are cation-dependent which suggests that noncovalent interactions are able to stabilize the water molecules favoring the Pt-H formation. Thus, in an interphase, in which the noncovalent interactions are more effective, HPRR will proceed as an indirect poisoned system, reflecting on slow frequency oscillations (omega), for instance omega(LiOH) < omega(NaOH) < omega(KOH) for several H2O2 concentrations.
Author(s): da Silva, KN (da Silva, Kaline N.); Nagao, R (Nagao, Raphael); Sitta, E (Sitta, Elton)
CHEMISTRYSELECT
Volume: 2 | Edição: 35 | Páginas: 11713-11716 | Publicado: DEC 11 2017
PDF: Alkali Cation Effect During the Oscillatory Electroreductionof H2O2on Pt
DOI: 10.1002/slct.201702276