Writers: R. M. Almeida; F. M. Matinaga; M. R. B. Andreeta; A. C. Hernandes; A. Dias; and R. L. Moreira
Keywords: Polymorphic-Induced Transformations; Laser-Heated Pedestal Growth
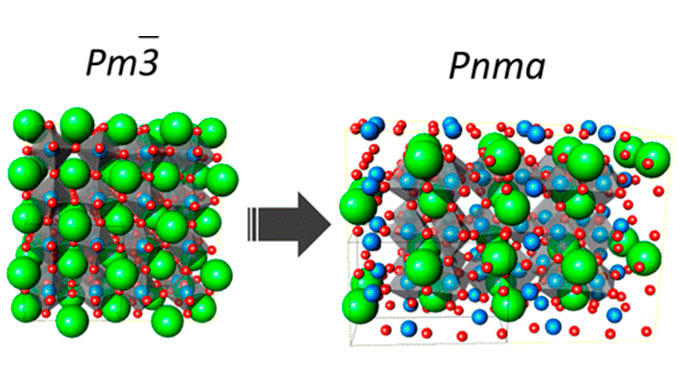
Abstract: Calcium tantalite (CaTa2O6) single crystal fibers were obtained by the laser-heated pedestal growth method (LHPG). At room temperature, this material can present three polymorphic modifications. The rapid crystallization inherent to the LHPG method produced samples within the Pm3̅ space group, with some chemical disorder. In order to check for polymorphic-induced transformations, the CaTa2O6 fibers have been submitted to different thermal treatments and investigated by micro-Raman spectroscopy. For short annealing times (15 min) at 1200 °C, the cubic modification was maintained, though with an improved crystalline quality, as evidenced by the enhanced inelastic scattered intensity (by ca. 250%) and narrowing of Raman bands. The polarized Raman spectra respected very well the predicted symmetries and the selection rules for this cubic modification. On the other hand, long annealing times (24 h) at 1200 °C led to a complete (irreversible) polymorphic transformation. The Raman bands became still more intense (ca. 15 times larger than for the as-grown fibers), narrower, and several new modes appeared. Also, the spectra became unpolarized, demonstrating a polycrystalline nature of the transformed crystals. The observed Raman modes could be fully assigned to an orthorhombic modification of CaTa2O6 belonging to the Pnma space group.
DOI: 10.1021/cg401078z