Flexible composite via rapid titania coating by microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis
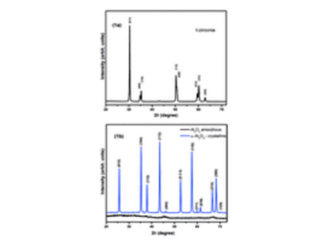
Abstract: The aim of this work was to prepare a flexible nanocomposite from ultra-fine titanium oxide (TiO2) growth on carbon fibre via microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis (MHS) and to evaluate its photocatalytic properties. The TiO2 nanoparticles were directly grown on the carbon fibre (CF). Thus, a study comparing the conventional titania coating vs. the MHS were performed. The significant layer interaction as a function of the coating method on the visible and dark dye photodegradation performance was observed. Techniques such as X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy (field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM)), Raman spectroscopy, among others were used aiming to characterize the different route samples. This study reports a reproducible and single method to manufacture of nanocomposites through the growth of TiO2 nanoparticle on CF by MHS that allow controlling the thickness layer. Similar procedure of synthesized nanocomposite could be applied in different chemical compositions to advanced applications, based on the electrochemical nanostructure.
Author(s): Marques E Silva, Ricardo; Thesing, Anderson; Deon, Vinicius Goncalves; et al.
Bulletin of Materials Science
Volume: 40 Issue: 3 Pages: 499-504 Published: 2017
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1396-y
PDF: Flexible composite via rapid titania coating by microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis