Writers: Roman Alvarez Roca; and Edson Roberto Leite
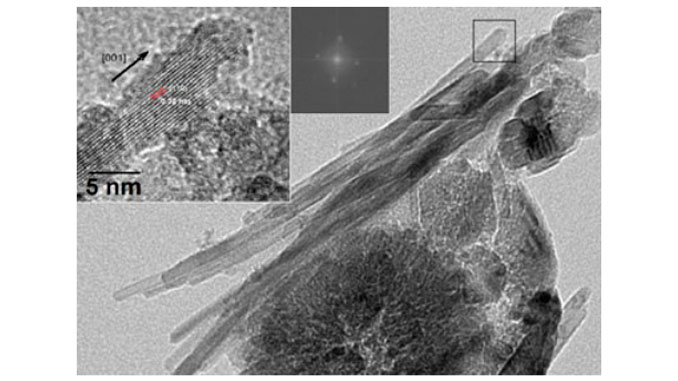
Abstract: A simple solvothermal low-temperature synthesis process of TiO2 nanoparticles was investigated in different solvents [Octanol (Oc), Ethanolamine (Am) and Terathane (Tr)] with titanium (IV) chloride (TiCl4) as precursor. The samples were characterized by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). XRD showed the crystallite size ranging from 4 to 12 nm, which were calculated using Debye–Scherrer’s equation. The existence of poor or high crystalline anatase phases and high crystalline anatase/rutile mixture was also shown. TEM images displayed variations in the morphological behavior depending on the synthesis condition. Particles of irregular morphology with high irregular agglomeration up to well-defined particles can be observed, which are self-assembled by oriented attachment (OA). This self-assembly led to TiO2 microparticles with 3-D Wulff shape for anatase and 1-D shape for rutile. The results showed that the TiO2 nanopowder could be easily engineered and adapted by the solvent type, the TiCl4 concentration and the synthesis time.
See PDF: Roca_et_al-2013-Journal_of_the_American_Ceramic_Society
DOI: 10.1111/jace.12078