Writers: Hercules Jorge ALMILHATTI, Karin Hermana NEPPELENBROEK, Carlos Eduardo VERGANI, Ana Lúcia MACHADO, Ana Cláudia PAVARINA, Eunice Teresinha GIAMPAOLO
Keywords: Dental materials; Dental alloys; Composite resins; Dental prosthesis.
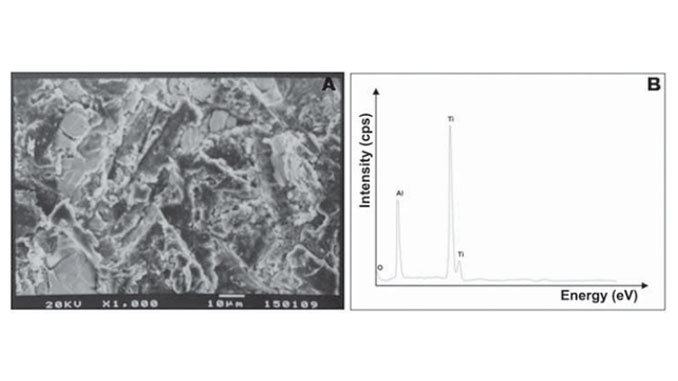
Abstract: Objective: This study evaluated the effect of three metal conditioners on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a prosthetic composite material to cpTi grade I having three surface treatments. Material and Methods: One hundred sixty eight rivet-shaped specimens (8.0×2.0 mm) were cast and subjected to polishing (P) or sandblasting with either 50 mm (50SB) or 250 mm (250SB) Al2O3. The metal conditioners Metal Photo Primer (MPP), Cesead II Opaque Primer (OP), Targis Link (TL), and one surface modification system Siloc (S), were applied to the specimen surfaces, which were covered with four 1-mm thick layers of resin composite. The resin layers were exposed to curing light for 90 s separately. Seven specimens from each experimental group were stored in water at 37ºC for 24 h while the other 7 specimens were subjected to 5,000 thermal cycles consisting of water baths at 4ºC and 60ºC (n=7). All specimens were subjected to SBS test (0.5 mm/min) until failure occurred, and further 28 specimens were analyzed using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Data were analyzed by 3-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test (α=0.05).
DOI: 10.1590/1679-775720130255